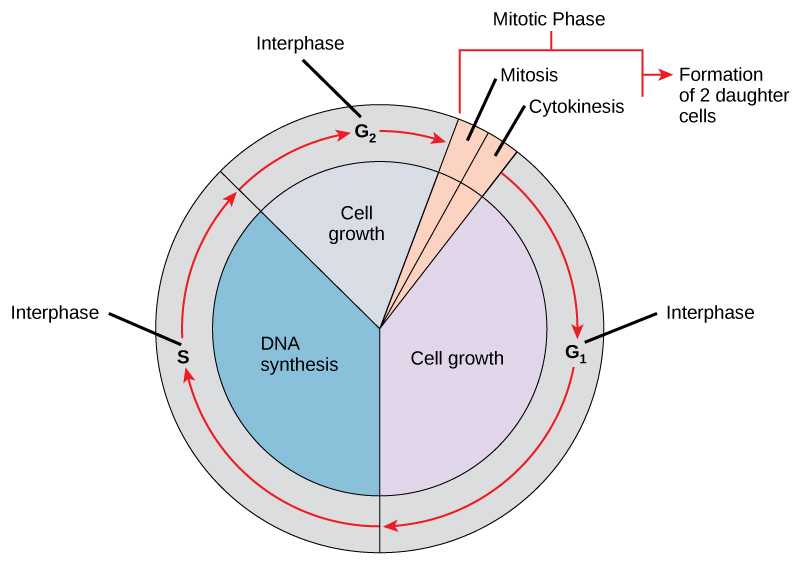
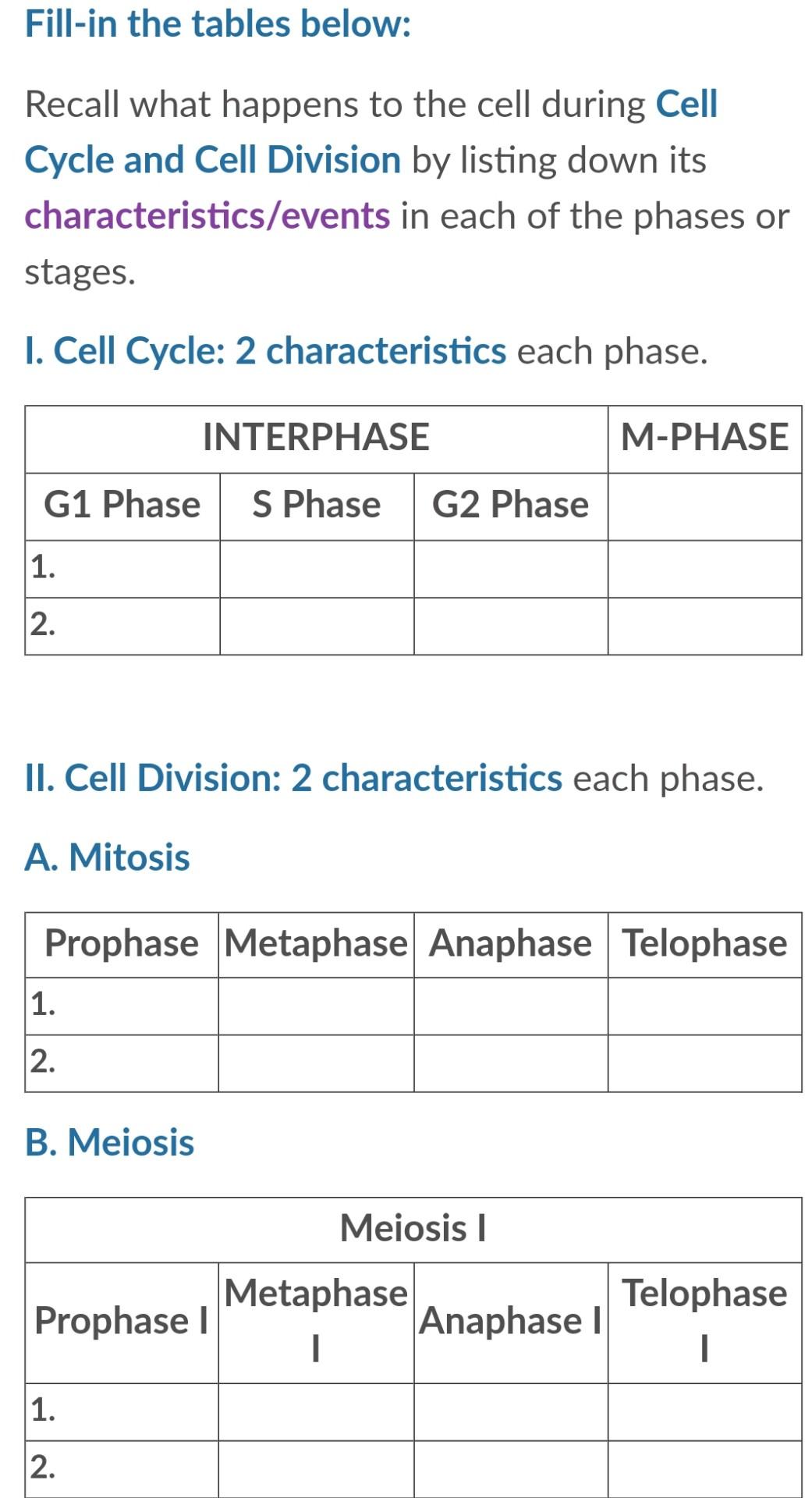
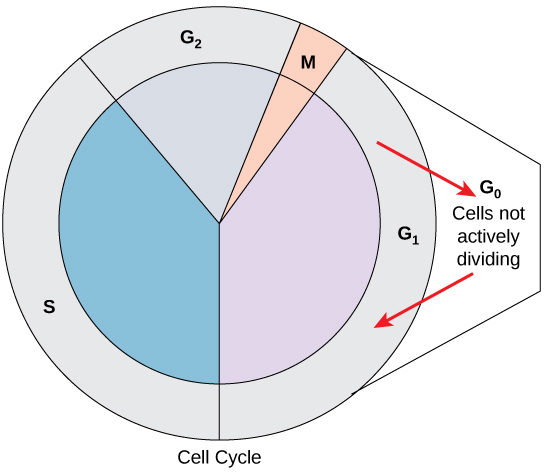
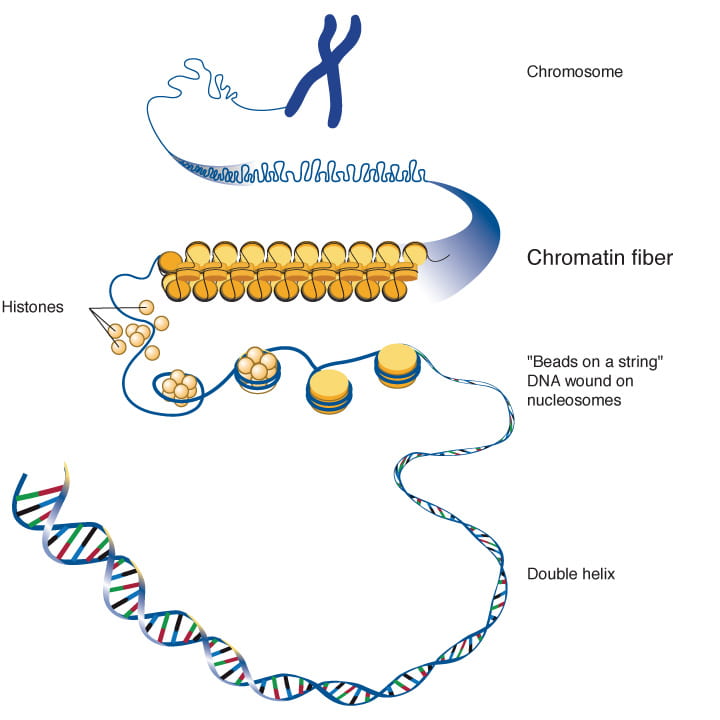
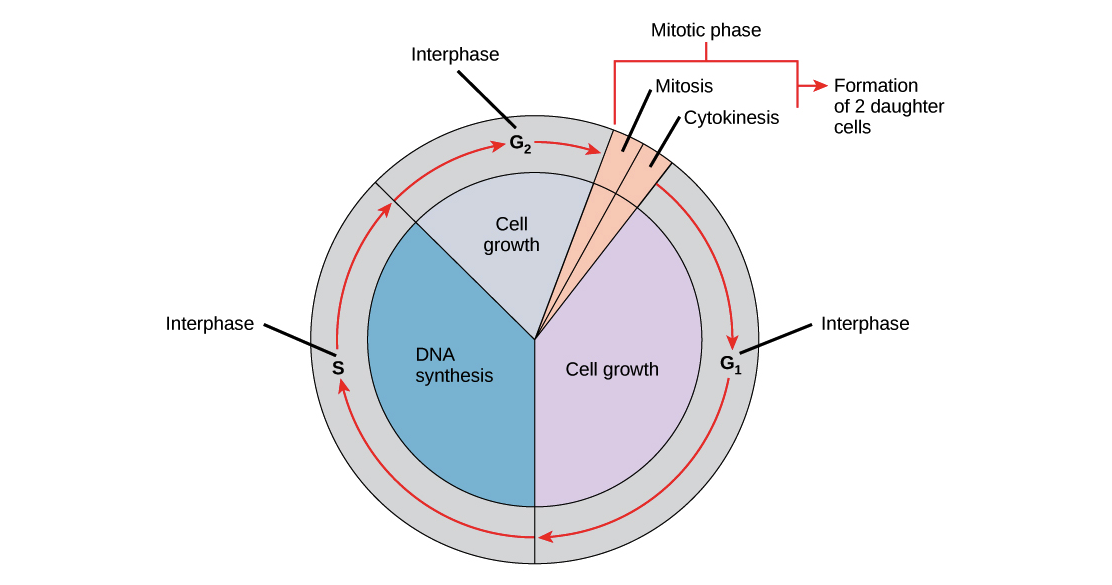
Cell Division B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, - ppt download

G1 cyclin–Cdk promotes cell cycle entry through localized phosphorylation of RNA polymerase II | Science
Meiotic Recombination Intermediates Are Resolved with Minimal Crossover Formation during Return-to-Growth, an Analogue of the Mitotic Cell Cycle | PLOS Genetics

G1-arrested newborn cells are the predominant infectious form of the pathogen Brucella abortus | Nature Communications

Week 13: Eukaryotic Cell Cycle Study Guide - The lectures for this week focus on the cell cycle in - Studocu
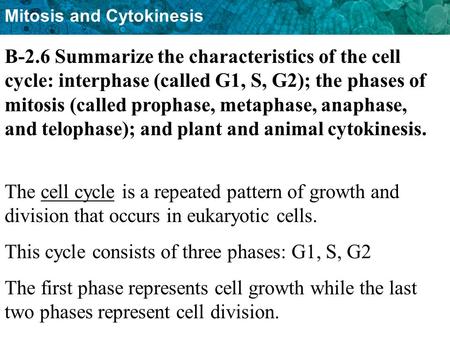
Cell Division B-2.6 Summarize the characteristics of the cell cycle: interphase (called G1, S, G2); the phases of mitosis (called prophase, metaphase, - ppt download
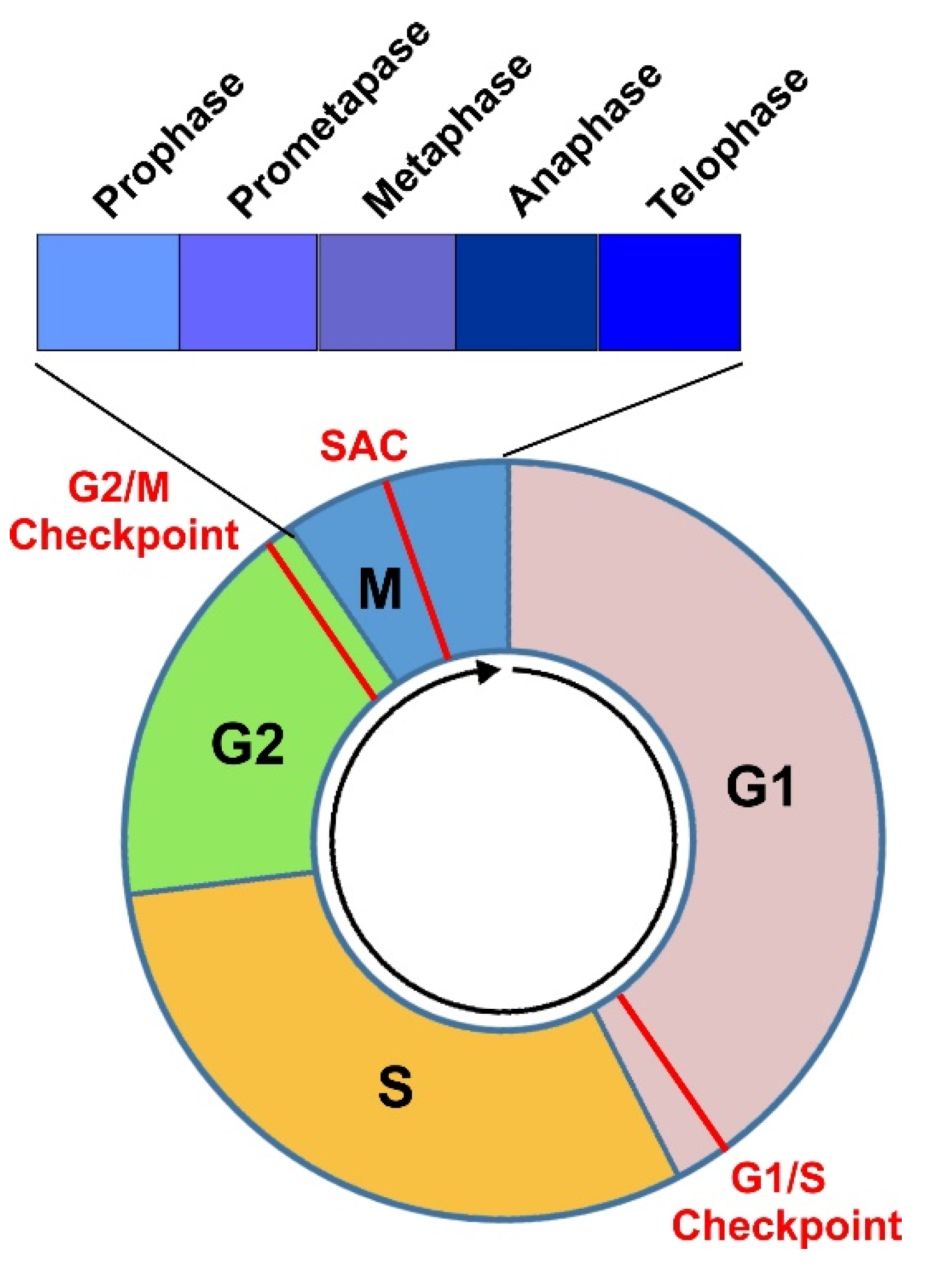
Cells | Free Full-Text | Regulation of Cell Cycle Progression by Growth Factor-Induced Cell Signaling